Models are part of MVC structure. They represent the rules and logic for an application. Means they hold data and define the validating rules for the data.
Model classes are extended by yii\base\Model or its child classes.
Mainly following features are implemented using models.
- attribute declaration
- attribute labels
- massive attribute assignment
- scenario-based validation
- can not embed HTML
- can not be directly accessed
Attributes
Attributes mainly represent the business data. Each attribute is a publicly accessible property of a model. They can be accessed like array elements or normal object properties. it is like publicly accessible properties of a model.
The method,
specifies what attributes a model class has.
Model class is also the base class for ActiveRecord class (which is an advanced model with additional functionality).
Attribute as a normal object property:
In earlier versions of Yii, scenarios and validation were handled with the same function. But in Yii2, they are split into different functions i.e; rules() and scenarios().
Here, rules() specify the validation of a data while scenarios() specify which attributes are safe to be assigned to the model.
Attribute Labels
Attribute labels are values which are displayed with attributes to get the input from the users.
For example, in the below code, ID, Name, Designation, Contact and Email denotes the attribute labels. All this is defined under a function attributeLabels().
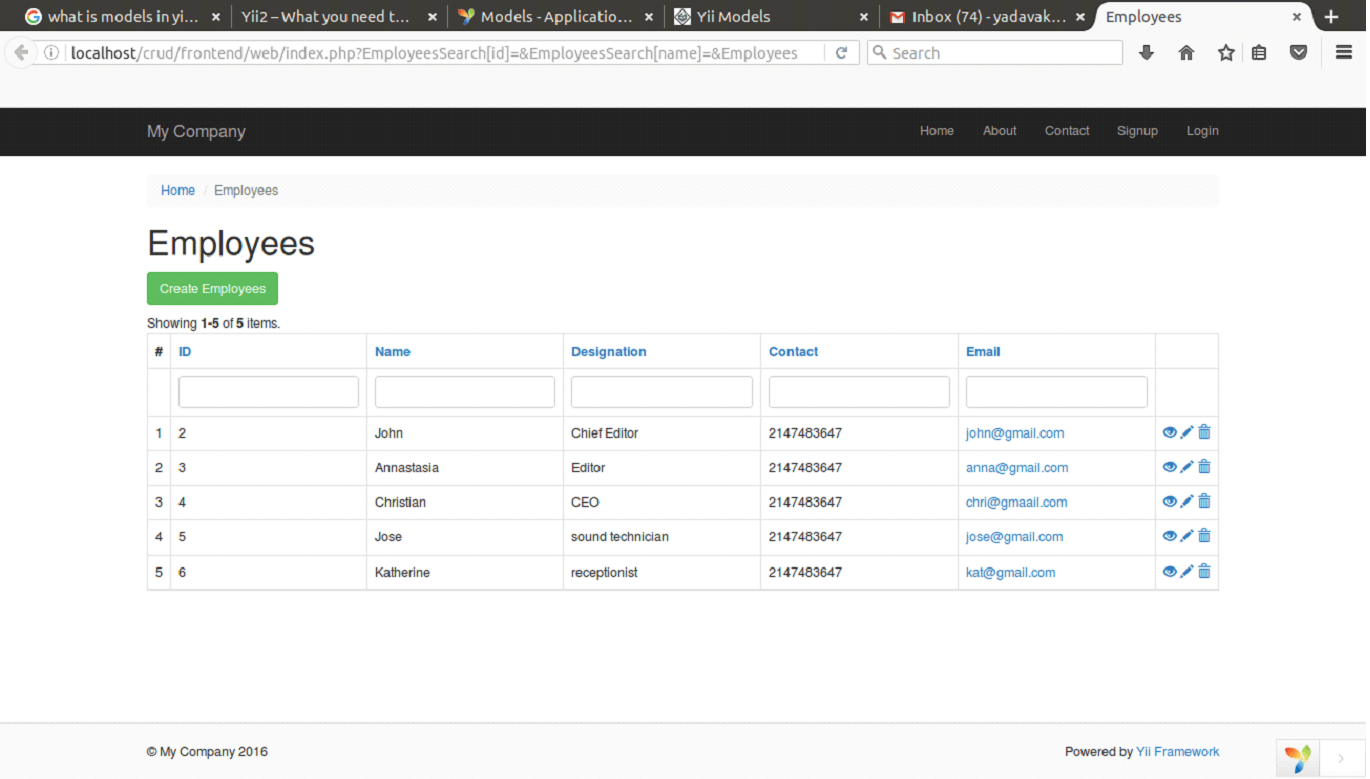
Look at the above snapshot, the heading data denotes the attribute labels.
Scenarios
A model may be used for different scenarios. For example, a model may be used to collect login user inputs while it may also be used to collect inputs of new users for registration. So in different scenarios a model may use different rules and logic.
Example
This is the ContactForm.php code,
Create an action actionContact in SiteController.php file
Now, we'll run the program in the browser,
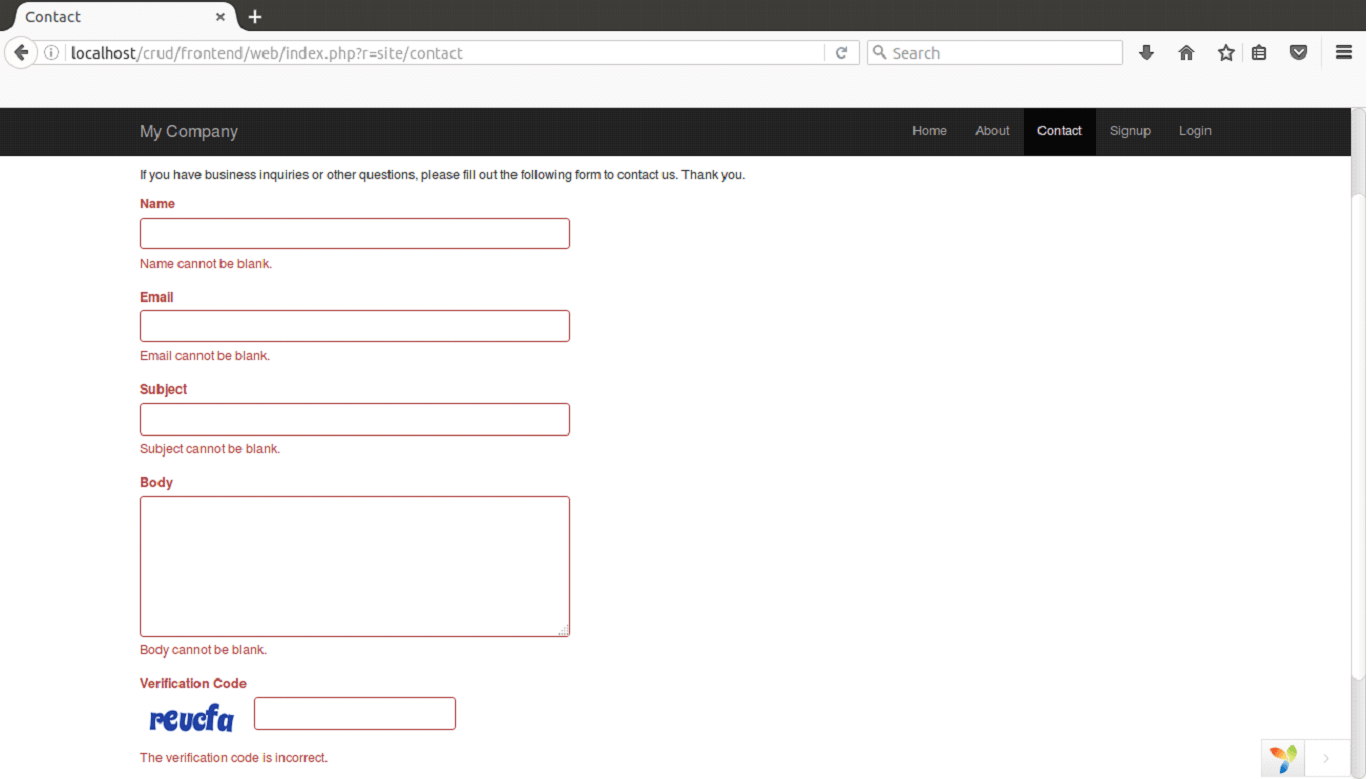
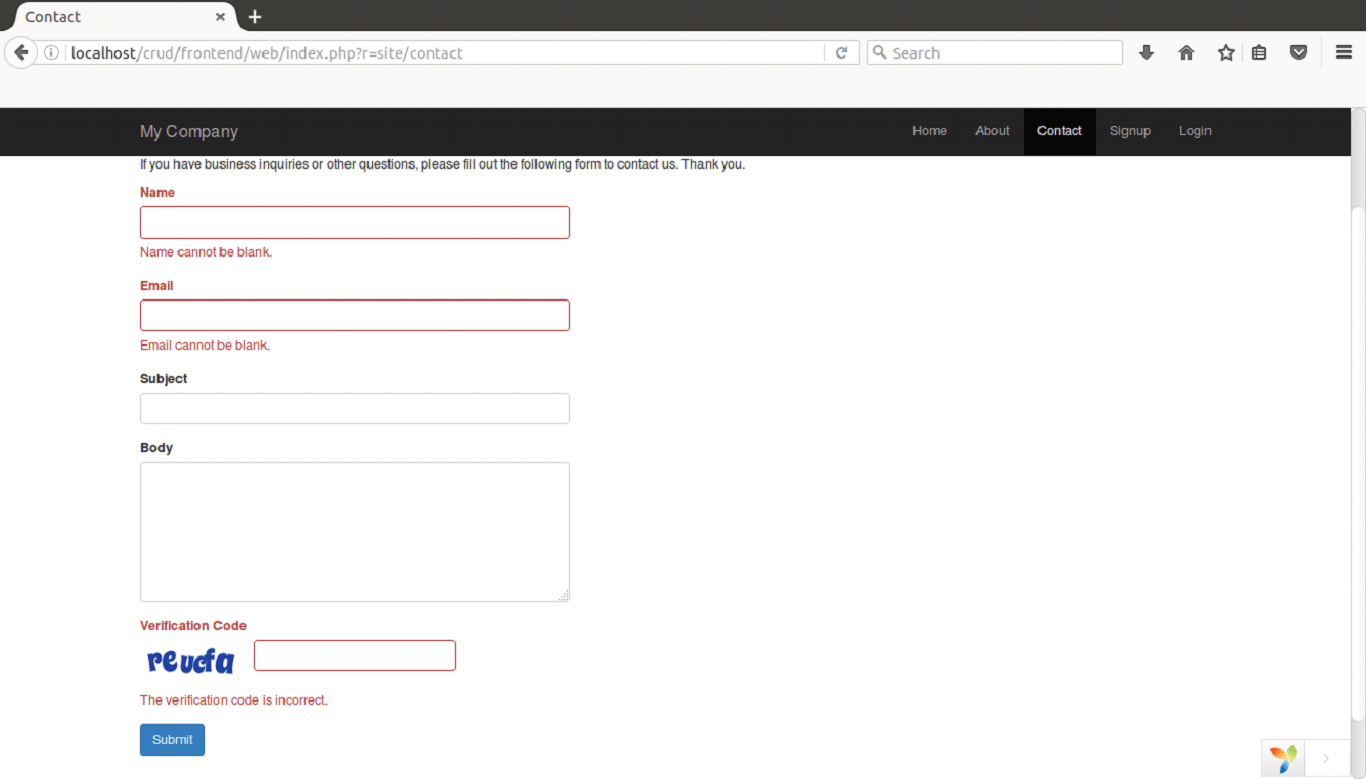
Now change the scenarion in actionContact in SiteController.php as
Now on running the program in the browser, Subject and Body field will be no longer required field.
Validation Rules
These are the rules which are set for the fields to be fulfilled by the users. For example, required rule will make sure that the respective field is not empty. And email attribute will make sure that the email entered is a valid email. If values do not satisfy the rules, an error message will appear on the screen.
To declare validation rules for all the fields in all the scenarios, following code is used.
The on property implements that, rule will be applied to a particular scenario. If you'll not use on property than by default rule will be applied for all the fields.
Massive Assignment
In massive assignment, a model is populated with user inputs using a single line of code. Massive assignment only applies to the safe attributes.
Look at the following two types of code, both assigning the submitted form data by the end users to attributes of the ContactForm model.
First one is,
The first one using massive assignment is much easier, neat and less error prone.



0 Comments