Mixin is a collection of CSS properties which facilitates you to add a bunch of properties from one rule-set into another rule-set and includes class names as its properties. These are similar to functions in programming languages. In Less, mixins can be declared as the same way as CSS style using class or id selector. It can store multiple values and can be reused in the code whenever necessary.
Mixin Output:
Usage of Less Mixin
|
Index |
Mixin |
Explanation |
|
1) |
Not Outputting the Mixin |
You can make a Mixin disappear in the output
by simply placing the parentheses after it. |
|
2) |
Selectors in Mixins |
The mixins can contain properties as well as
selectors. |
|
3) |
Namespaces |
Namespaces are used to group the mixins
under common name. |
|
4) |
Guarded Namespaces |
If the applied guard?s condition to
namespace returns true then the mixins defined by it are used. |
|
5) |
The !important keyword |
the !important keyword is used to override
the particular property. |
Let's take an example
to demonstrate the use of mixins in Less file.
Create a HTML file
named "simple.html", having the following data.
HTML file: simple.html
Now create a file named "simple.less". It is similar to CSS file. The only one difference is that it is saved with ".less" extension.
Less file: simple.less
Put the both file "simple.html" and "simple.less" inside the root folder of Node.js
Now, execute the following code: lessc simple.less simple.css
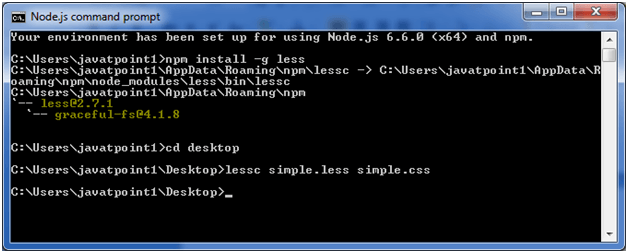
This will compile the "simple.less" file. A CSS file named "simple.css" will be generated.
For example:
This will compile the "simple.less" file. A CSS file named "simple.css" will be generated.
For example:
The generated CSS "simple.css", has the following code:
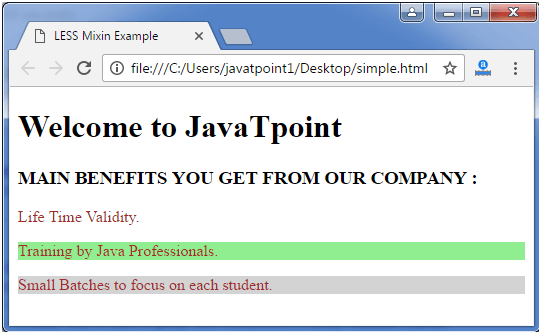
Output:



0 Comments