ArrayList and Vector both implements List interface and maintains insertion order.
However, there are many differences between ArrayList and Vector classes that are given below.
|
ArrayList |
Vector |
|
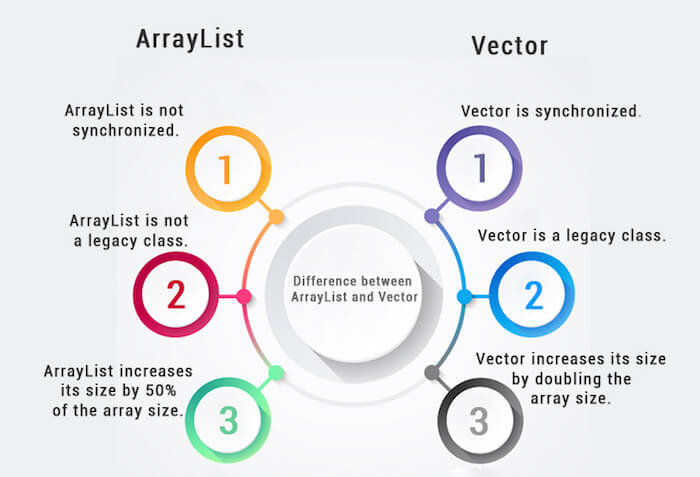
1) ArrayList is not synchronized. |
Vector is synchronized. |
|
2) ArrayList increments 50% of
current array size if the number of elements exceeds from its capacity. |
Vector increments 100% means
doubles the array size if the total number of elements exceeds than its
capacity. |
|
3) ArrayList is not a legacy class.
It is introduced in JDK 1.2. |
Vector is a legacy class. |
|
4) ArrayList is fast because
it is non-synchronized. |
Vector
is slow because it is synchronized, i.e., in a
multithreading environment, it holds the other threads in runnable or
non-runnable state until current thread releases the lock of the object. |
|
5) ArrayList uses the Iterator interface
to traverse the elements. |
A Vector can use the Iterator interface
or Enumeration interface to traverse the elements. |
Example of Java ArrayList
Let's see a simple example where we are using ArrayList to store and traverse the elements.
Output:
Sonoo Michael James Andy
Example of Java Vector
Let's see a simple example of a Java Vector class that uses the Enumeration interface.
Output:
umesh irfan kumar



0 Comments