The throw and throws is the concept of exception handling where the throw keyword throw the exception explicitly from a method or a block of code whereas the throws keyword is used in signature of the method.
There are many differences between throw and throws keywords. A list of differences
between throw and throws are given below:
|
Sr. no. |
Basis of Differences |
throw |
throws |
|
1. |
Definition |
Java throw keyword
is used throw an exception explicitly in the code, inside the function or the
block of code. |
Java throws keyword
is used in the method signature to declare an exception which might be thrown
by the function while the execution of the code. |
|
2. |
Type of exception
Using throw keyword, we can only propagate unchecked exception i.e., the
checked exception cannot be propagated using throw only. |
Using throws
keyword, we can declare both checked and unchecked exceptions. However, the
throws keyword can be used to propagate checked exceptions only. |
|
|
3. |
Syntax |
The throw keyword
is followed by an instance of Exception to be thrown. |
The throws keyword
is followed by class names of Exceptions to be thrown. |
|
4. |
Declaration |
throw is used
within the method. |
throws is used with
the method signature. |
|
5. |
Internal
implementation |
We are allowed to
throw only one exception at a time i.e. we cannot throw multiple exceptions. |
We can declare
multiple exceptions using throws keyword that can be thrown by the method.
For example, main() throws IOException, SQLException. |
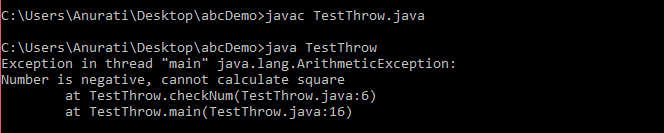
Java throw Example
TestThrow.java
Output:
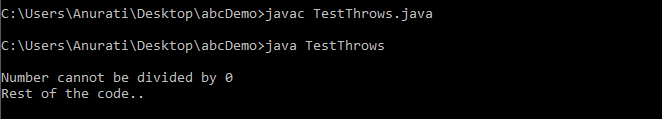
Java throws Example
TestThrows.java
Output:
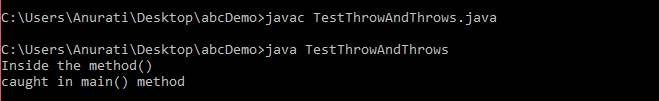
Java throw and throws Example
TestThrowAndThrows.java
Output:



0 Comments