Software testing tutorial provides basic and advanced concepts of software testing. Our software testing tutorial is designed for beginners and professionals.
Software testing is widely used technology because it is compulsory to test each and every software before deployment.
Our Software testing tutorial includes all topics of Software testing such as Methods such as Black Box Testing, White Box Testing, Visual Box Testing and Gray Box Testing. Levels such as Unit Testing, Integration Testing, Regression Testing, Functional Testing. System Testing, Acceptance Testing, Alpha Testing, Beta Testing, Non-Functional testing, Security Testing, Portability Testing.
Content List:
Software Testing
- Software Testing Principles
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
- Types of Software Testing
- Levels of Testing
- Test Maturity Model
SDLC models
Types of Testing
Types of Manual
White Box Techniques
- Data Flow Testing
- Control Flow Testing
- Branch Coverage Testing
- Statement Coverage Testing
- Decision Coverage Testing
Black Box Techniques
- Decision table technique in Black box testing
- All-pairs Testing
- Cause and Effect Graph in Black box Testing
- State Transition Technique
- Use Case Technique
Types of Black Box
Types of Functional
Types of Non-Functional
Test Case Development
Testing Techniques
Test Management
Defect Tracking
- Bug in Software Testing
- Bug Life cycle
- Severity and Priority in testing
- What is the test environment?
- Defect Management Process
Other Types of Testing
- Regression Testing
- Smoke Testing
- Sanity Testing
- Static Testing
- Dynamic Testing
- Load Testing
- Stress Testing
- Recovery Testing
- Exploratory Testing
- Visual Testing
- Acceptance Testing
- Alpha Testing Introduction
- Beta Testing
- Database Testing
- Mainframe Testing
- Adhoc Testing
- Globalization Testing
- Mutation Testing
- Security Testing
- Accessibility Testing
- Structural Testing
- Volume Testing
- Scalability Testing
- Stability Testing
- Spike Testing
- Negative Testing
- Positive Testing
- Endurance Testing
- Reliability Testing
- Monkey Testing
- Agile Testing
- Component Testing
- GUI Testing
- Test Strategy
Software Testing Tools
- Software Testing Tools
- Test Management Tool
- Defect/Bug tracking tool
- Automation testing tool
- Performance testing tools (Load testing tools)
- Cross-browser testing tools
- Integration testing tools
- Unit testing tools
- Mobile Testing Tools
- GUI testing tools
- Security testing tools
- Penetration Testing Tools
Differences
- Automation Testing vs. Manual Testing
- Load Testing vs. Stress Testing
- Differences Between Smoke Testing and Sanity Testing
- Difference Between System Testing and Acceptance Testing
- Quality Assurance vs Quality Control
- Static Testing vs. Dynamic Testing
- Verification and Validation Testing
- Differences Between Alpha Testing and Beta Testing
- Black Box Testing vs. White Box Testing vs. Grey Box Testing
- Difference Between Globalization Testing and Localization Testing
- Test Case Vs. Test Scenarios
- Test Plan VS. Test Strategy
- Difference between Boundary value analysis & Equivalence partitioning
- Difference between Bug, Defect, Error, Fault & Failure
- SDLC VS. STLC
- Difference Between Testing and Debugging
- Frontend Testing VS. Backend Testing
- Difference Between HLD and LLD
- BRS vs SRS
- Difference Between Positive Testing and Negative Testing
- Difference Between Top-Down and Bottom-Up Integration Testing
- Monkey Testing VS Gorilla Testing
- Difference Between Stubs and Drivers
- Difference Between Component Testing and Unit Testing
- Differences Between Software Testing and Embedded Testing
- Differences Between GUI Testing and Usability Testing
- The Difference between SDET and Tester
- Differences Between Desktop Application testing, Client-Server Application Testing and Web Application Testing
What is Software Testing
Software testing is a process of identifying the correctness of software by considering its all attributes (Reliability, Scalability, Portability, Re-usability, Usability) and evaluating the execution of software components to find the software bugs or errors or defects.
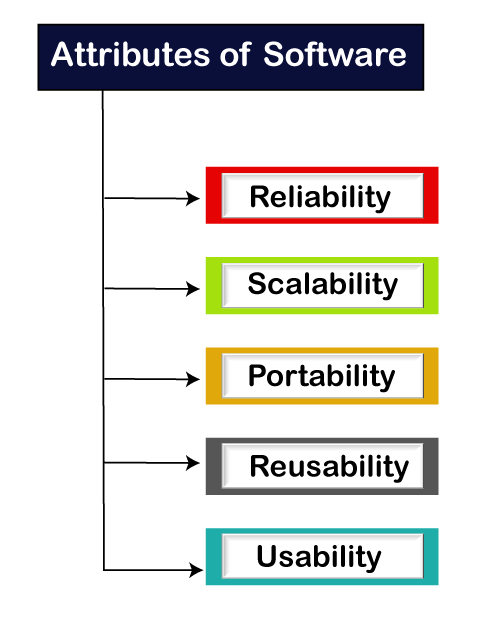
Software testing provides an independent view and objective of the software and gives surety of fitness of the software. It involves testing of all components under the required services to confirm that whether it is satisfying the specified requirements or not. The process is also providing the client with information about the quality of the software.
Testing is mandatory because it will be a dangerous situation if the software fails any of time due to lack of testing. So, without testing software cannot be deployed to the end user.
What is Testing
Testing is a group of techniques to determine the correctness of the application under the predefined script but, testing cannot find all the defect of application. The main intent of testing is to detect failures of the application so that failures can be discovered and corrected. It does not demonstrate that a product functions properly under all conditions but only that it is not working in some specific conditions.
Testing furnishes comparison that compares the behavior and state of software against mechanisms because the problem can be recognized by the mechanism. The mechanism may include past versions of the same specified product, comparable products, and interfaces of expected purpose, relevant standards, or other criteria but not limited up to these.
Testing includes an examination of code and also the execution of code in various environments, conditions as well as all the examining aspects of the code. In the current scenario of software development, a testing team may be separate from the development team so that Information derived from testing can be used to correct the process of software development.
The success of software depends upon acceptance of its targeted audience, easy graphical user interface, strong functionality load test, etc. For example, the audience of banking is totally different from the audience of a video game. Therefore, when an organization develops a software product, it can assess whether the software product will be beneficial to its purchasers and other audience.
Type of Software testing
We have various types of testing available in the market, which are used to test the application or the software.
With the help of below image, we can easily understand the type of software testing:
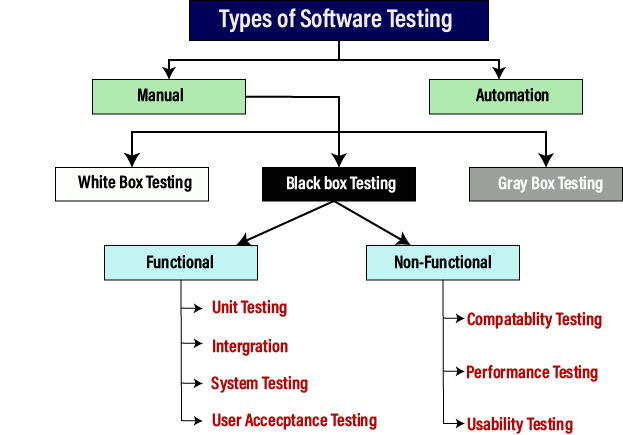
Manual testing
The process of checking the functionality of an application as per the customer needs without taking any help of automation tools is known as manual testing. While performing the manual testing on any application, we do not need any specific knowledge of any testing tool, rather than have a proper understanding of the product so we can easily prepare the test document.
Manual testing can be further divided into three types of testing, which are as follows:
- White box testing
- Black box testing
- Gray box testing
Automation testing
Automation testing is a process of converting any manual test cases into the test scripts with the help of automation tools, or any programming language is known as automation testing. With the help of automation testing, we can enhance the speed of our test execution because here, we do not require any human efforts. We need to write a test script and execute those scripts.
Prerequisite
Before learning software testing, you should have basic knowledge of basic computer functionality, basic mathematics, computer language, and logical operators.
Audience
Our software testing tutorial is designed for beginners and professionals.
Problems
We assure that you will not find any problem in this Software Testing Tutorial. But if there is any mistake, please post the problem in contact form.



0 Comments